Learning Through Art Water Molecules and Hydrogen Bonding
A molecule within the bulk of a liquid experiences attractions to neighboring molecules in all directions but since these average out to zero there is no net force on the molecule. Reactants and products in reversible and irreversible chemical reactionsWatch the next lesson.
Solved Learning Through Art Water Molecules And Hydrogen Chegg Com
Learning through art water molecules and hydrogen bonding.

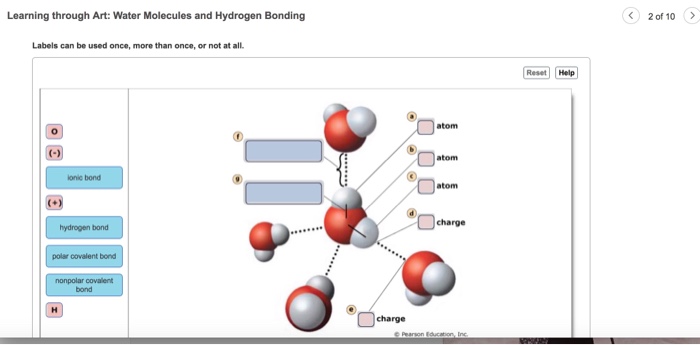
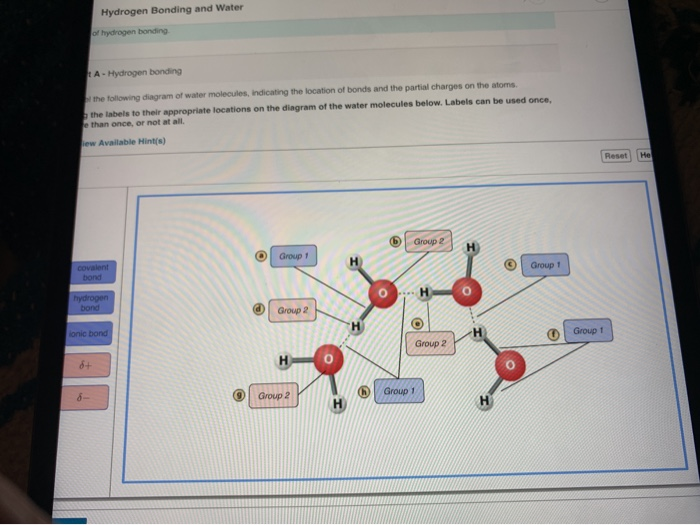
. A hydrogen atom attached to a relatively electronegative atom is a hydrogen bond donor. Water Molecules and Hydrogen Bonding Can you label the atoms partial charges and types of bonds associated with these water molecules. Here the hydrogen bond acceptor is the π electron cloud of a benzene ring.
The key to understanding waters chemical behavior is its molecular structure. Hydrogen Bonding in Water art A e figure shows how water forms hydrogen bonds. View the full answer.
Learning through art water molecules and hydrogen bonding Identify the compounds that engage in hydrogen bonding as pure liquids. Can you label the atoms partial charges and types of bonds associated with these water molecules. Hydrogen bonding is responsible for ammonias remarkably high solubility in water.
1 Water the molecule. This hydrogen bonding can be clearly seen in the structure of pure ice. View Available Hints The CH4 molecule exhibits hydrogen bonding.
Its strength per mole of hydrogen bonds ranges from 4 kJ to 50 kJ. A hydrogen bond is possible with only certain hydrogen-containing. Sec20Bio131BIDA Signed in as Ania Rivers Help Close Chapter 2.
Water also forms hydrogen bonds with itself called. Reset Help I Hydrogen Slightly negative charge Water molecule Oxygen Slightly positive. The water molecules within pure ice form hydrogen bonds with each other creating a perfect lattice structure as seen in the image below.
Water readily sticks to many other substances a. A water molecule consists of two hydrogen atoms bonded to an oxygen atom and its overall structure is bent. Its oxygen atom has a slightly negative charge and its hydrogen atoms each have a slightly positive charge.
Check all that apply. First use pink labels to identify the atoms and. Hydrogen bonding is strong and directed resulting in shorter interatomic distances and a small number of interaction partners.
Correct Hydrogen bonds form weak attractions between neighboring water molecules. Up to 256 cash back Get the detailed answer. Molecules 02 Post Lecture alkthrough.
Many organic carboxylic acids form hydrogen-bonded dimers in the solid state. Hydrogen bonding is an electrostatic dipole-to-dipole contact between molecules that shares certain covalent bonding characteristics. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
This electronegative atom is usually fluorine oxygen or nitrogenThe electronegative atom attracts the electron cloud from around the hydrogen nucleus and by decentralizing the cloud leaves the hydrogen atom with a positive partial charge. In H 2 O only two of the six outer-shell electrons of oxygen are used for this purpose leaving four electrons which are organized into two non-bonding pairs. Learning through art water molecules and hydrogen bonding.
Part A Watch the animation and identify the correct conditions for forming a hydrogen bond. The electrons within a water atom spend much more time circling the oxygen atom than the hydrogen atoms. When water molecules from hydrogen bond with other molecules the process is called adhesion.
Part A Drag the labels to their appropriate locations in this diagram. A hydrogen bond in water occurs between the hydrogen atom of one water molecule and the lone pair of electrons on an oxygen atom of a neighboring water molecule. In water each hydrogen nucleus is covalently bound to the central oxygen atom by a pair of electrons that are shared between them.
This creates a high surface tension of water. The special properties of water come from the fact that the elements hydrogen and oxygen have differing electronegativities. A hydrogen bond is an intermolecular attractive force in which a hydrogen atom that is covalently bonded to a small highly electronegative atom is attracted to a lone pair of electrons on an atom in a neighboring.
The hydrogen atom has a positive charge well the oxygen atom has a. As the temperature of the water molecules rise they move faster temperature is a measure of how fast the average particle is moving and thus its momentum. As the molecules vibrate more and move around more the energy necessary to disrupt the hydrogen bonds is achieved by more a.
View Homework Help - MasteringBiology_ Chapter 2 HWhtml from BIOLOGY 131 at Henry Ford College. Ag the labels to their appropriate locations on the figure. This is because the oxygen atom in addition to forming bonds with the hydrogen atoms also carries two pairs of unshared electrons.
Free unlimited access for 30 days limited time only. This type of interaction is important in maintaining the shape of proteins. Answer 1 of 2.
In Chapter 3 we learned that covalent bonds formed between atoms of differing electronegativity are polarized. In fact the hydrogen bonds between molecules. Because electronegativity is a measure of how strongly a given atom attracts electrons to itself the atom in the covalent.
Solved Hydrogen Bonding And Water Of Hydrogen Bonding A Chegg Com

Mastering Biology 2 Flashcards Quizlet
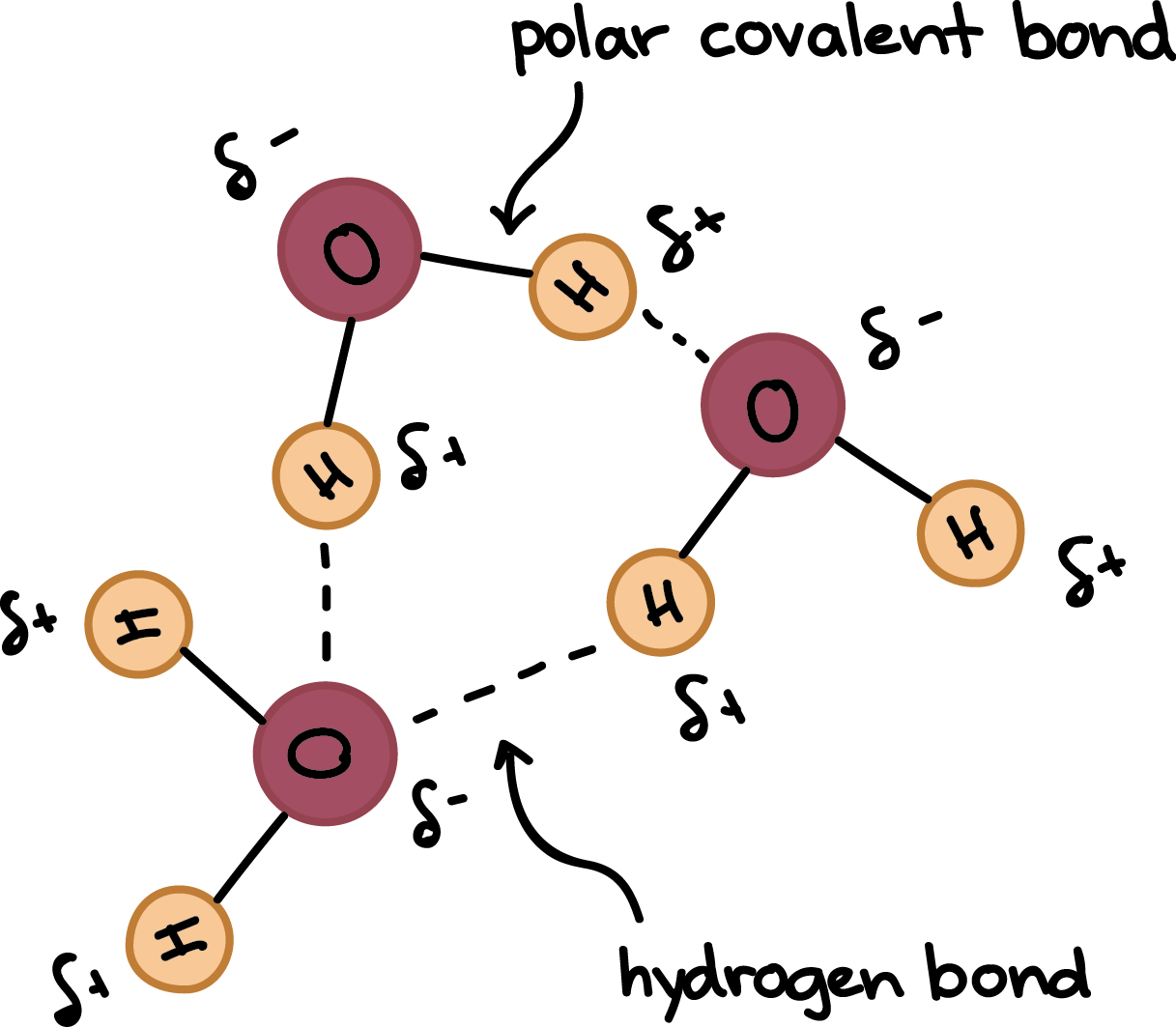

Comments
Post a Comment